Test module#
This section presents how to create a Test module and add it into the Swan project using the Python API. In the example below, the project includes two modules: a module body and a Test module.
Note
Project dependencies are not supported yet. You should add the dependencies manually.
Create a Test module#
Using the ScadeOne class, create a new project:
from ansys.scadeone.core import ScadeOne
from ansys.scadeone.core.svc.swan_creator import ScadeOneFactory
app = ScadeOne()
project_path = Path(r"project1\project1.sproj")
project = app.new_project(project_path)
Once the project is created, add a module body:
m_body = project.add_module_body("module0")
Update the module body by adding a textual operator definition:
op1_str = """
function operator0 (a: int32;
b : int32;)
returns (c: int16;)
{
diagram
(let c = (a:>int16) * 256 + (b:>int16);)
}
"""
m_body = project.add_module_body("module0")
# Add an operator definition to module0
opt0 = m_body.add_textual_operator_definition(op1_str)
After creating the project, also add a Test module:
# Add a Test module
m_test = project.add_test_module("module1")
Once the Test module is created, add a set sensor, an operator under test, a data source, an oracle and connections between blocks, as shown in the following diagram:
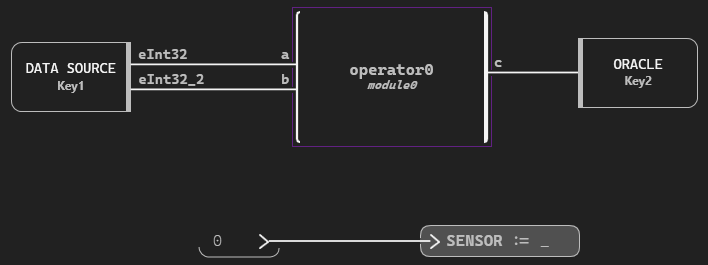
The corresponding code is:
# Add a sensor to module
sensor = m_test.add_sensor("SENSOR", "int32")
# Add a test harness to module1
opt = m_test.add_test_harness("harness0")
# Use directive module0
use = m_test.use("module0")
# Add under test instance
diag1 = opt.add_diagram()
op_def = m_body.operator_definitions[0]
under_test = diag1.add_instance_under_test(op_def)
# Add set sensor
set_sensor = diag1.add_set_sensor(sensor)
cst1 = m_test.add_constant("cst1", "int32", "0")
expr = diag1.add_expr_block(cst1)
# Add data source
data_source = diag1.add_data_source("Key1")
# Add oracle
oracle = diag1.add_oracle("Key2")
# Wire connections
wire0 = diag1.connect((data_source, "eInt32"), (under_test, "a"))
wire1 = diag1.connect((data_source, "eInt32_2"), (under_test, "b"))
wire2 = diag1.connect(under_test, (oracle, "c"))
wire3 = diag1.connect(expr, set_sensor)
Finally, save the project, and look at the generated code:
project.save()
# Print all .swan* files in assets folder
for m in project_path.parent.glob("assets/*.swan*"):
print(f"{'=' * 20}\nModule: {m.name}\n{'=' * 20}")
print(m.read_text())
Complete example#
This is the complete script presenting a Scade One model creation.
from pathlib import Path
from ansys.scadeone.core import ScadeOne
from ansys.scadeone.core.svc.swan_creator import ScadeOneFactory
app = ScadeOne()
project_path = Path(r"project1\project1.sproj")
project = app.new_project(project_path)
module_factory = ScadeOneFactory().module
# Add a module body
op1_str = """
function operator0 (a: int32;
b : int32;)
returns (c: int16;)
{
diagram
(let c = (a:>int16) * 256 + (b:>int16);)
}
"""
m_body = project.add_module_body("module0")
# Add an operator definition to module0
opt0 = m_body.add_textual_operator_definition(op1_str)
# Add a Test module
m_test = project.add_test_module("module1")
# Add a sensor to module
sensor = m_test.add_sensor("SENSOR", "int32")
# Add a test harness to module1
opt = m_test.add_test_harness("harness0")
# Use directive module0
use = m_test.use("module0")
# Add under test instance
diag1 = opt.add_diagram()
op_def = m_body.operator_definitions[0]
under_test = diag1.add_instance_under_test(op_def)
# Add set sensor
set_sensor = diag1.add_set_sensor(sensor)
cst1 = m_test.add_constant("cst1", "int32", "0")
expr = diag1.add_expr_block(cst1)
# Add data source
data_source = diag1.add_data_source("Key1")
# Add oracle
oracle = diag1.add_oracle("Key2")
# Wire connections
wire0 = diag1.connect((data_source, "eInt32"), (under_test, "a"))
wire1 = diag1.connect((data_source, "eInt32_2"), (under_test, "b"))
wire2 = diag1.connect(under_test, (oracle, "c"))
wire3 = diag1.connect(expr, set_sensor)
# Save project
project.save()
# Print all .swan* files in assets folder
for m in project_path.parent.glob("assets/*.swan*"):
print(f"{'=' * 20}\nModule: {m.name}\n{'=' * 20}")
print(m.read_text())
